Popcorn Hack: Which of the following lines will cause an error?
public class SnackDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Snack choiceOne = new Snack("cookies", 100);
Snack choiceTwo = new Snack();
System.out.println(choiceOne.getName());
System.out.println(choiceOne.getCalories());
choiceTwo.setName("chips");
choiceTwo.calories = 150;
}
}
choiceTwo.calories = 150; should give an error. This is because you’re trying to access the calories field of the Snack object directly. If calories is a private field in the Snack class, you won’t be able to access it directly from outside the class.
Create a Book class where each book has a title, genre, author, and number of pages. Include a default and overloaded constructor.
public class Book {
private String title;
private String genre;
private String author;
private int numberOfPages;
// Default constructor
public Book() {
this.title = "";
this.genre = "";
this.author = "";
this.numberOfPages = 0;
}
// Overloaded constructor
public Book(String title, String genre, String author, int numberOfPages) {
this.title = title;
this.genre = genre;
this.author = author;
this.numberOfPages = numberOfPages;
}
// Getter methods
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public String getGenre() {
return genre;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public int getNumberOfPages() {
return numberOfPages;
}
// Setter methods
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public void setGenre(String genre) {
this.genre = genre;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public void setNumberOfPages(int numberOfPages) {
this.numberOfPages = numberOfPages;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
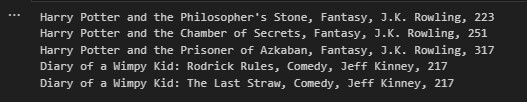
Book book1 = new Book("Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone", "Fantasy", "J.K. Rowling", 223);
Book book2 = new Book("Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets", "Fantasy", "J.K. Rowling", 251);
Book book3 = new Book("Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban", "Fantasy", "J.K. Rowling", 317);
Book book4 = new Book("Diary of a Wimpy Kid: Rodrick Rules", "Comedy", "Jeff Kinney", 217);
Book book5 = new Book("Diary of a Wimpy Kid: The Last Straw", "Comedy", "Jeff Kinney", 217);
System.out.println(book1.getTitle() + ", " + book1.getGenre() + ", " + book1.getAuthor() + ", " + book1.getNumberOfPages());
System.out.println(book2.getTitle() + ", " + book2.getGenre() + ", " + book2.getAuthor() + ", " + book2.getNumberOfPages());
System.out.println(book3.getTitle() + ", " + book3.getGenre() + ", " + book3.getAuthor() + ", " + book3.getNumberOfPages());
System.out.println(book4.getTitle() + ", " + book4.getGenre() + ", " + book4.getAuthor() + ", " + book4.getNumberOfPages());
System.out.println(book5.getTitle() + ", " + book5.getGenre() + ", " + book5.getAuthor() + ", " + book5.getNumberOfPages());
}
}
Main.main(null);
### POPCORN HACKS: write an accessor method for each of the instance variables:
public class Course {
private String name;
private String gradeLevel;
private int period;
// Accessor method for 'name'
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// Accessor method for 'gradeLevel'
public String getGradeLevel() {
return this.gradeLevel;
}
// Accessor method for 'period'
public int getPeriod() {
return this.period;
}
}
Create a Java class BankAccount to represent a simple bank account. This class should have the following attributes:
accountHolder (String): The name of the account holder. balance (double): The current balance in the account. Implement the following mutator (setter) methods for the BankAccount class:
Ensure that the balance is never negative.
public class BankAccount {
private String accountHolder;
private double balance;
// Constructor
public BankAccount(String accountHolder, double balance) {
this.accountHolder = accountHolder;
this.balance = balance;
}
// Setter for accountHolder
public void setAccountHolder(String accountHolder) {
this.accountHolder = accountHolder;
}
// Method to deposit an amount
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
this.balance += amount;
}
}
// Method to withdraw an amount
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount > 0 && amount <= this.balance) {
this.balance -= amount;
}
}
// Getter for balance
public double getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a bank account for Alice with an initial balance of $1000
BankAccount aliceAccount = new BankAccount("Alice", 1000.00);
// Deposit $500 into Alice's account
aliceAccount.deposit(500.00);
// Create a bank account for Bob with an initial balance of $2000
BankAccount bobAccount = new BankAccount("Bob", 2000.00);
// Withdraw $300 from Bob's account
bobAccount.withdraw(300.00);
// Print the balances
System.out.println("Alice's balance: " + aliceAccount.getBalance());
System.out.println("Bob's balance: " + bobAccount.getBalance());
}
}
Main.main(null);
Create a Java class MathUtility with a set of utility methods for mathematical operations. Implement the following methods:
public class MathUtility {
// Calculate the average of an array of numbers
public static double calculateAverage(double[] numbers) {
if (numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Array must not be null or empty");
}
double sum = 0;
for (double num : numbers) {
sum += num;
}
return sum / numbers.length;
}
// Check if a given integer is prime
public static boolean isPrime(int number) {
if (number <= 1) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Find and return an array of factors for a given integer
public static int[] findFactors(int number) {
if (number <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number must be greater than 0");
}
int[] factors = new int[number];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
factors[count] = i;
count++;
}
}
int[] result = new int[count];
System.arraycopy(factors, 0, result, 0, count);
return result;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Calculate the average of an array of numbers
double[] numbers = {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0};
double average = MathUtility.calculateAverage(numbers);
System.out.println("Average: " + average);
// Check if a number is prime
int number = 7;
boolean isPrime = MathUtility.isPrime(number);
System.out.println("Is " + number + " prime? " + isPrime);
// Find and print the factors of a number
number = 12;
int[] factors = MathUtility.findFactors(number);
System.out.print("Factors of " + number + ": ");
for (int factor : factors) {
System.out.print(factor + " ");
}
}
}
Main.main(null);
Make the code a little clearer by using the this keyword
b,a,w,and s aren’t meaningful parameters change them into breed, age, weight, and score
distinguish the local and instance variables using the this keyword
public class Dog {
private String breed;
private int age;
private double weight;
private double score;
public Dog(String breed, int age, double weight, double score){
this.breed = breed;
this.age = age;
this.weight = weight;
this.score = score;
}
}